Intuitionistic fuzzy RFE-based prognostic model for liver transplantation
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Survival prediction after liver transplantation is a very challenging but complex task. LT is often the best treatment for advanced liver disease, provided no other medical conditions contraindicate it. This article explores clinical predictors, such as MELD scores and hormone levels, along with computational algorithms for forecasting post-transplant survival.
Objective: This study evaluates the performance of machine learning models for predicting survival outcomes in liver transplant recipients using UNOS data. It develops and validates a donor and recipient-based prognostic model.
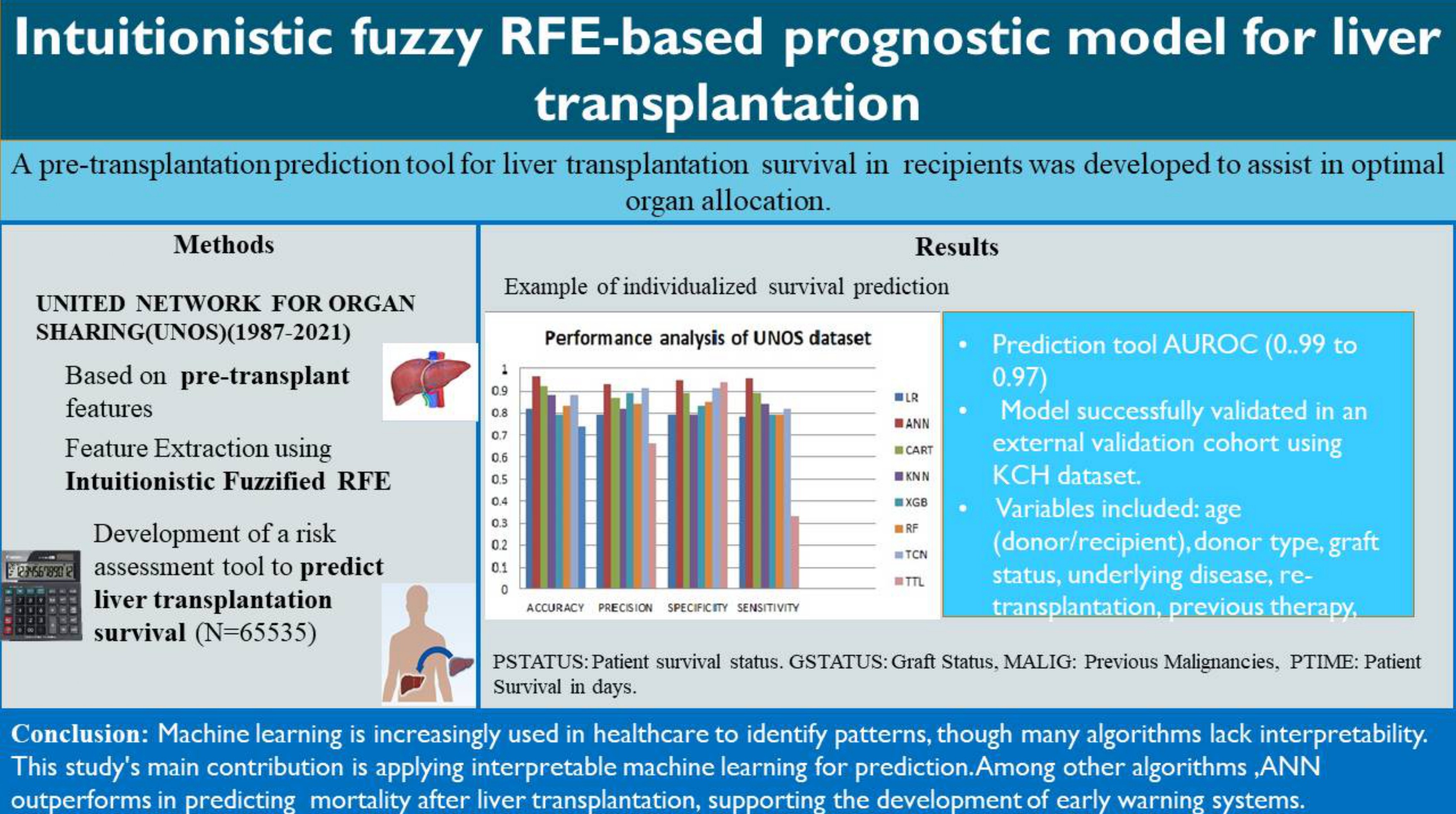
Materials and methods: The UNOS database contains 65,535 donor-recipient pairs in transplants conducted in the U.S. between October 1987 and June 2021, with 421 attributes. The top 24 features, including logistic regression, random forest, artificial neural networks, XGBoost, CART, and K-nearest neighbors, were used to train the models upon feature selection. Models were compared using AUROC, accuracy, specificity, sensitivity, and precision.
Results: ANN outperformed other models for the UNOS dataset, with an AUROC of 0.98–0.99. Validated results in the KCH dataset are robust at AUROC: 0.94–0.95.
Conclusion: The model offered exceptional generalizability performance to guide clinical decisions in transplantation support, yet variability in patients’ characteristics may differ significantly among the cohorts and impact the results.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP, Nartey YA, Pose E, Kamath PS. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 Update. J Hepatol. 2023; 79(2): 516-37. doi: 10.1016/ j.jhep.2023.03.017.
Schulz MS, Gu W, Schnitzbauer AA, Trebicka J. Liver transplantation as a cornerstone treatment for acute-on-chronic liver failure. Transpl Int. 2022; 3 5 : 10108. doi: 10.3389/ti.2022.10108. PMID: 35572467, PMCID: PMC9099355.
Park HS, Lee JM, Hong K, Han ES, Hong SK, Choi Y, et al. Impact of model for end-stage liver disease allocation system on outcomes of deceased donor liver transplantation: A single-center experience. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021; 25(3): 336-41. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.3.336.
Artru F, Samuel D. Approaches for patients with very high MELD scores. JHEP Rep. 2019; 1(1): 53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2019.02.008. Erratum in: JHEP Rep. 2019; 1(5): 414. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2019.10.002, PMID: 32039352, PMCID: PMC7001538.
Molinari M, Jorgensen D, Subhashini Ayloo, Stalin Dharmayan, Christof Kaltenmeier, Mehta RB, et al. Preoperative Stratification of Liver Transplant Recipients: Validation of the LTRS. Transplantation. 2020; 104(12): e332-e41. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/articles/PMC8015433/.
Raji CG, Vinod Chandra SS. Long-term forecasting the survival in liver transplantation using multilayer perceptron networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. 2017; 47(8): 2318-29. doi: 10.1109/ TSMC.2017.2661996.
Georgios Kantidakis, Putter H, Lancia C, J. de Boer, Braat AE, Fiocco M. Survival prediction models since liver transplantation - comparisons between Cox models and machine learning techniques. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020; 20(1): 277. doi.org/10.1186/ s12874-020-01153-1.
Wang YC, Yong CC, Lin CC, Alam H, Naseer F, Lin YH, et al. Excellent outcome in living donor liver transplantation: Treating patients with acute-onchronic liver failure. Liver Transpl. 2021; 27(11): 1633-43. doi: 10.1002/lt.26096.
Jung S, Park K, Ihn K, et al. Predicting graft failure in pediatric liver transplantation based on early biomarkers using machine learning models. Sci Rep. 2022; 12: 22411. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25900-0.
Tran J, Sharma D, Gotlieb N, et al. Application of machine learning in liver transplantation: a review. Hepatol Int. 2022; 16(3): 495-508. doi: 10.1007/ s12072-021-10291-7.
Gibb S, Berg T, Herber A, Isermann B, Kaiser T. A new machine-learning-based prediction of survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. J Lab Med. 2023; 47(1): 13-21. doi: 10.1515/labmed-2022-0162.
Nitski, O., Azhie, A., Qazi-Arisar, F. A., Wang, X., Ma, S., Lilly, L., et al. Long-term mortality risk stratification of liver transplant recipients: Real-time application of deep learning algorithms on longitudinal data. Lancet. 2021; Volume 3(5): E295-E305. doi.org/10.1016/S25 89-7500(21)00040-6.
Atanassov KT. On intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Springer; 2012. European Scientific Journal. 2014; 10(15): ISSN: 1857-7881.
Pandey K, Mishra A, Rani P, Ali J, Ripon Chakrabortty. Selecting features by utilizing intuitionistic fuzzy Entropy method. DMAME. 2023; 6(1): 111-33.
Yanagawa R, Iwadoh K, Akabane M, Imaoka Y, Bozhilov KK, Melcher ML, et al. Light GBM outperforms other machine learning techniques in predicting graft failure after liver transplantation: Creation of a predictive model through large-scale analysis. Clin Transplant. 2024; 38(4): e15316. https://pubmed. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38607291/.
Javaid M,Haleem A,Singh RP, Suman R, Rab S. Significance of machine learning in healthcare: Features, pillars and applications. Int J Intell Netw. 2022; 3(2): 58-73. doi.org/10.1016/j.ijin.2022.05. 002.
Awad M, Fraihat S. Recursive feature elimination with cross-validation with decision tree: Feature selection method for machine learning-based intrusion detection systems. J Sens Actuator Netw. 2023; 12(5): 67. Available from: https://www.mdpi. com/2224-2708/12/5/67.
Xu D, Sheng JQ, Hu PJ, Huang TS, Lee WC. Predicting hepatocellular carcinoma recurrences: a data-driven multiclass classification method incorporating latent variables. J Biomed Inform. 2019; 96: 103237. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103237.
Sutton CD. Classification and regression trees, bagging, and boosting. In: Rao CR, Wegman EJ, Solka JL, editors. Handbook of statistics. Vol. 24. Elsevier; 2005. p. 303-29.
Faraggi D, Simon R. A neural network model for survival data. Stat Med. 1995; 14(1): 73-82.
Bradley AP. The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 1997; 30(7): 1145-59. doi.org/10. 1016/S0031-3203(96)00142-2.
Ali N, Neagu D, Trundle P. Evaluation of k-nearest neighbour classifier performance for heterogeneous data sets. SN Appl Sci. 2019; 1: 1559.
Fatemi Y, Nikfar M, Oladazimi A, Zheng J, Hoy H, Ali H. Machine learning approach for cardiovascular death prediction among nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) liver transplant recipients. Healthcare (Basel). 2024; 12(12). doi: 10.3390/healthcare12121165.
Guijo-Rubio D, Briceño J, Gutiérrez PA, Ayllón MD, Ciria R, Hervás-Martínez C. Statistical methods versus machine learning techniques for donorrecipient matching in liver transplantation. Stepkowski S, Editor. PLOS ONE. 2021; 16(5): e0252068. doi.org/10. 1371/journal.pone.0252068.
Spann A, Yasodhara A, Kang J, Watt K, Wang B, Goldenberg A, et al. Applying machine learning in liver disease and transplantation: A comprehensive review. Hepatology. 2020; 71(3): 1093-105. doi: 10. 1002/hep.31103.
Ahsan MM, Siddique Z. Machine learning-based heart disease diagnosis: a systematic literature review. Artif Intell Med. 2022; 128: 102289. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102289.
Yu Y, Peng C, Zhang Z, Shen K, Zhang Y, Xiao J, et al. Machine learning methods for predicting long-term mortality in patients after cardiac surgery. FrontCardiovasc Med. 2022; 9: 831390. doi.org/10.3389/ fcvm.2022.831390.
Wakjira TG, Khan IA, Usama Ebead, Alam MS. Explainable machine learning model and reliability analysis for flexural capacity prediction of RC beams strengthened in flexure with FRCM. Eng Struct. 2022; 255: 113903. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.113903.