Psychometric properties of the self-report questionnaire on occupational balance in university students with game addiction
Main Article Content
Abstract
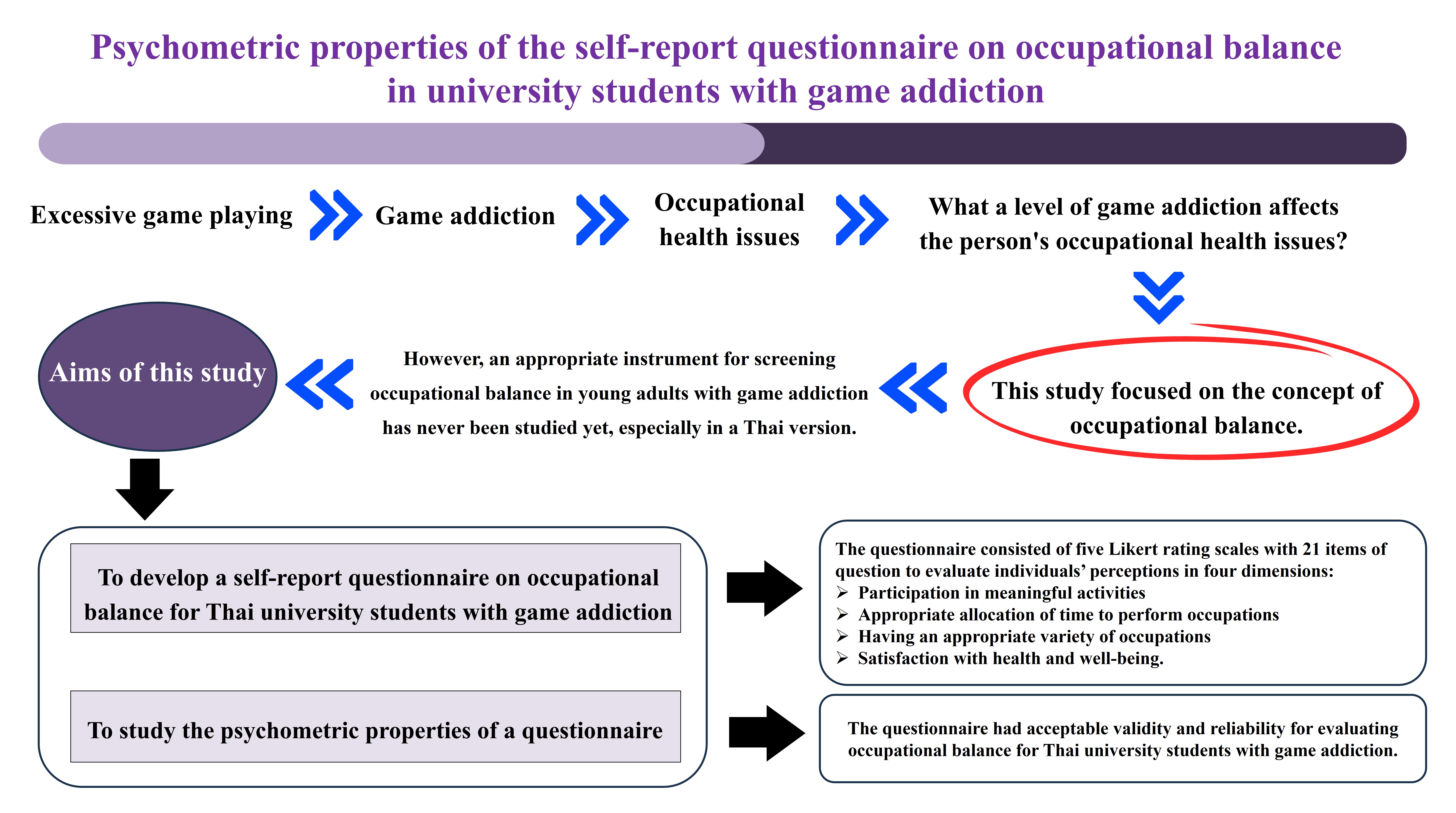
Background: The prevalence of adolescents and young adults playing games on the internet is increasing worldwide. However, excessive game playing can cause game addiction among adolescents. Studies have demonstrated that game addiction increases the risks of physical and mental health problems, leading to occupational performance issues. Nevertheless, what level of game addiction impacts occupational health issues is controversial. Therefore, this study focused on occupational balance, an individual’s perception of a proper amount and diversity of activities. The study demonstrated that occupational imbalance could lead to a decrease in an individual’s occupational performance. However, an appropriate instrument for screening occupational balance in young adults with game addiction has never been studied yet, especially in a Thai version.
Objective: This study aimed to develop a self-report questionnaire on occupational balance for Thai university students with game addiction.
Materials and methods: The questionnaire consisted of 21 items divided into four dimensions, including the individual’s perceptions of participating in meaningful activities, having the proper proportion of time to perform occupations, having the appropriate variety of professions, and being satisfied with their health and well-being. In addition, the psychometric properties of a questionnaire were investigated.
Results: The questionnaire had sufficient validity and good internal consistency for screening occupational balance in Thai university students with game addiction. The questionnaire was divided into four dimensions, each with good construct validity and internal consistency.
Conclusion: The questionnaire was valid and reliable for evaluating occupational balance for Thai university students with game addiction. This information can provide a new occupational therapy instrument for identifying occupational balance in the population with game addiction.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Kim D, Lee J. Addictive Internet Gaming Usage among Korean Adolescents before and after the Outbreak of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comparison of the Latent Profiles in 2018 and 2020. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18(14). doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147275
Basdas O, Ozbey H. Digital game addiction, obesity, and social anxiety among adolescents. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2020; 34(2): 17-20. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2019. 12.010
Regier DA, Kuhl EA, Kupfer DJ. The DSM-5: Classification and criteria changes. World Psychiatry. 2013; 12(2): 92-8. doi: 10.1002/wps.20050
Gao YX, Wang JY, Dong GH. The prevalence and possible risk factors of internet gaming disorder among adolescents and young adults: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J Psychiatr Res. 2022; 154: 35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.06.049
Zhao W, Wei T, Zhou R, Wang Y, Wang Y, Ren Z, et al. The Influence of Online Game Behaviors on the Emotional State and Executive Function of College Students in China. Front Psychiatry. 2021; 12: 713364. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.713364
Dong G, Li H, Wang L, Potenza MN. Cognitive control and reward/loss processing in Internet gaming disorder: Results from a comparison with recreational Internet game-users. Eur Psychiatry. 2017; 44: 30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.03.004
Alghamdi FAD, Alghamdi FAG, Abusulaiman A, Alsulami AJ, Bamotref M, Alosaimi A, et al. Video Game Addiction and its Relationship with Sleep Quality among Medical Students. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2024; 19: 1-8. doi: 10.1007/s44197-024-00265-x
Yang SY, Wang YC, Lee YC, Lin YL, Hsieh PL, Lin PH. Does Smartphone Addiction, Social Media Addiction, and/or Internet Game Addiction Affect Adolescents’ Interpersonal Interactions? Healthcare. 2022; 23;10: 963-77. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10050963
Van den Eijnden R, Koning I, Doornwaard S, van Gurp F, Ter Bogt T. The impact of heavy and disordered use of games and social media on adolescents’ psychological, social, and school functioning. J Behav Addict. 2018; 7(3): 697-706. doi: 10.1556/2006.7. 2018.65
Bavelier D, Green CS, Han DH, Renshaw PF, Merzenich MM, Gentile DA. Brains on video games. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011; 12(12): 763-8. doi: 10.1038/nrn3135
Feng J, Spence I, Pratt J. Playing an action video game reduces gender differences in spatial cognition. Psychol Sci. 2007; 18(10): 850-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1467- 9280.2007.01990.x
Martin Perez AM, Maximo-Bocanegra N, Rivas Ruiz F, Alguacil-Diego IM, Martinez-Piedrola RM. [Occupational balance, disability and functionality in people with rheumatic disease]. An Sist Sanit Navar. 2023; 46(3): e1053-62. doi: 10.23938/ASSN.1053
Magnusson L, Hakansson C, Brandt S, Oberg M, Orban K. Occupational balance and sleep among women. Scand J Occup Ther. 2021; 28(8): 643-51. doi: 10.1080/11038128.2020.1721558
Hakansson C, Ahlborg G, Jr. Occupational imbalance and the role of perceived stress in predicting stressrelated disorders. Scand J Occup Ther. 2018; 25(4): 278-87. doi: 10.1080/11038128.2017.1298666
AA. W. An occupational perspective of health. 2nd ed. ed: Thorofare, NJ: Slack.; 2006.
Nurit W, Michal AB. Rest: a qualitative exploration of the phenomenon. Occup Ther Int. 2003; 10(4): 227- 38. doi: 10.1002/oti.187
Wagman P, Hakansson C, Bjorklund A. Occupational balance as used in occupational therapy: a concept analysis. Scand J Occup Ther. 2012; 19(4): 322-7. doi: 10.3109/11038128.2011.596219
Backman CL. Occupational balance: exploring the relationships among daily occupations and their influence on well-being. Can J Occup Ther. 2004; 71(4): 202-9. doi: 10.1177/000841740407100404
Dur M, Steiner G, Fialka-Moser V, Kautzky-Willer A, Dejaco C, Prodinger B, et al. Development of a new occupational balance-questionnaire: incorporating the perspectives of patients and healthy people in the design of a self-reported occupational balance outcome instrument. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014; 12: 45. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-12-45
Wagman P, Hakansson C. Introducing the Occupational Balance Questionnaire (OBQ). Scand J Occup Ther. 2014; 21(3): 227-31. doi: 10.3109/11038128.2014. 900571
Pornnoppadol P. SB, Khamklieng K., Pattana-amorn S. The Development of Game Addiction Screening Test (GAST). J Psychiatr Assoc Thailand. 2014; 59(1): 3-14.
Bujang MA, Omar ED, Baharum NA. A Review on Sample Size Determination for Cronbach’s Alpha Test: A Simple Guide for Researchers. Malays J Med Sci. 2018; 25(6): 85-99. doi: 10.21315/mjms2018.25.6.9
Hammell KW. Dimensions of meaning in the occupations of daily life. Can J Occup Ther. 2004; 71(5): 296-305. doi: 10.1177/000841740407100509
Khiaw-Im N, Aimyong N, Wongrathanandha C, Tangsangwornthamma C. Cross-Cultural Adaptation, Reliability, and Content Validity of Thai Version of Workplace Violence in the Health Sector Country Case Study Questionnaire. J Prim Care Community Health. 2022; 13: 1-5. doi: 10.1177/21501319221132448
Kim M, Yeom HE, Jung MS. Validation and psychometric properties of the multidimensional scale of perceived social support among Korean breast cancer survivors. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2022; 9(4): 229-35. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2022.01.004
Green SB, Yang Y, Alt M, Brinkley S, Gray S, Hogan T, et al. Use of internal consistency coefficients for estimating reliability of experimental task scores. Psychon Bull Rev. 2016; 23(3): 750-63. doi: 10.3758/ s13423-015-0968-3
Townsend E, Wilcock AA. Occupational justice and client-centred practice: a dialogue in progress. Can J Occup Ther. 2004; 71(2): 75-87. doi: 10.1177/00084 1740407100203
Hinkamp D, Morton J, Krasnow DH, Wilmerding MV, Dawson WJ, Stewart MG, et al. Occupational Health and the Performing Arts: An Introduction. J Occup Environ Med. 2017; 59(9): 843-58. doi: 10.1097/JOM. 0000000000001052
Gulu M, Yagin FH, Gocer I, Yapici H, Ayyildiz E, Clemente FM, et al. Exploring obesity, physical activity, and digital game addiction levels among adolescents: A study on machine learning-based prediction of digital game addiction. Front Psychol. 2023; 14: 1097145. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1097145
Labana RV, Hadjisaid JL, Imperial AR, Jumawid KE, Lupague MJM, Malicdem DC. Online Game Addiction and the Level of Depression Among Adolescents in Manila, Philippines. Cent Asian J Glob Health. 2020; 9(1): e369. doi: 10.5195/cajgh.2020.369
Zaman M, Babar MS, Babar M, Sabir F, Ashraf F, Tahir MJ, et al. Prevalence of gaming addiction and its impact on sleep quality: A cross-sectional study from Pakistan. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022; 78: 103641. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103641
Yildiz Durak H, Haktanir A, Saritepeci M. Examining the Predictors of Video Game Addiction According to Expertise Levels of the Players: The Role of Time Spent on Video Gaming, Engagement, Positive Gaming Perception, Social Support and Relational Health Indices. Int J Ment Health Addict. 2023; 9: 1-26. doi: 10.1007/s11469-023-01073-3
Guszkowska M, Dabrowska-Zimakowska A. Occupational balance, changes in occupations and psychological well-being of university students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Scand J Occup Ther. 2023; 30(4): 463-74. doi: 10.1080/11038128.2022.2143892
WHO Guideline on Self-Care Interventions for Health and Well-Being. WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. Geneva2021.