Urine Biomarkers of Tubular Injury Predict Outcomes in Diabetic Nephropathy: A Prospective Cohort Study
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Currently available biomarkers, such as serum creatinine and albuminuria, exhibit low sensitivity in predicting renal progression. Novel biomarkers of tubular injury may aid in identifying patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) at high risk for renal progression. This study evaluates the potential of urine biomarkers of tubular damage in predicting renal progression and the composite outcome of renal progression and death in T2DM.
Methods: This prospective cohort study involved 257 patients with T2DM. Urine biomarkers of tubular injury were assessed at baseline. The outcomes examined were the composite renal outcome of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), a 40% decline in eGFR, and death.
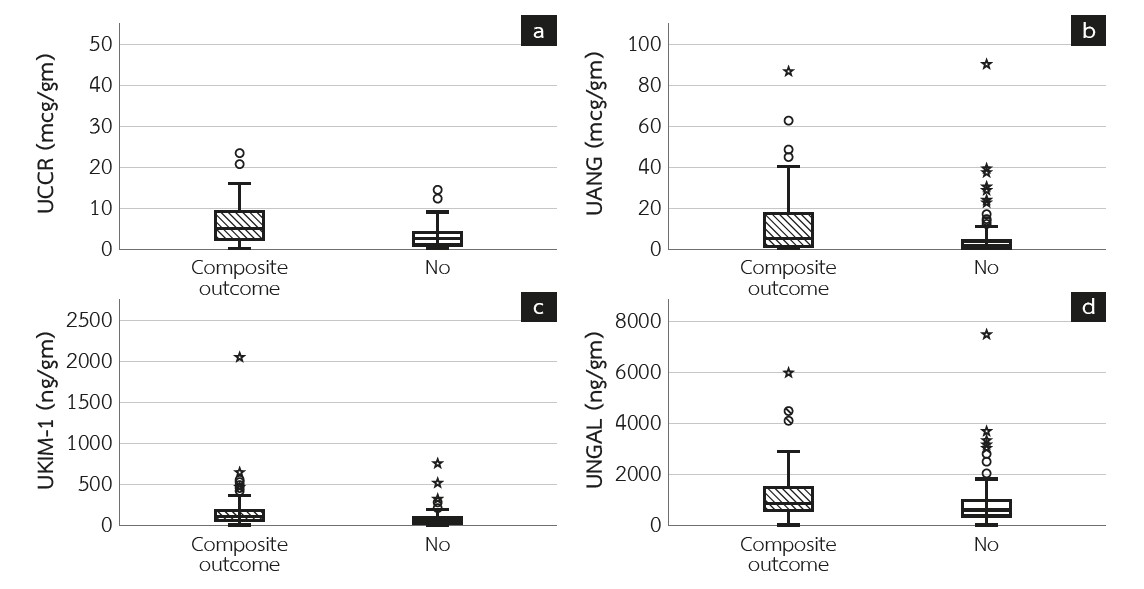
Results: Most patients were in chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages 3 and 4, with a median urine albumin/creatinine ratio of 60.8 mg/g. The median follow-up duration was 7 years. Baseline urine concentrations of cystatin-C, angiotensinogen, kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), and neutrophil-gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) were significantly higher among patients who reached the composite renal outcome. All tubular biomarkers demonstrated intermediate predictive performance for the composite renal outcome, with area under the curve (AUC) values ranging between 0.65 and 0.72, comparable to urine albumin/creatinine. Using the optimal cut-off value for each urine biomarker, higher levels were significantly associated with the composite renal outcome. However, when employing an adjusted Cox proportional hazards model for the composite renal endpoint across the quartiles of urine tubular biomarker levels, only the upper quartiles of urine cystatin-C and KIM-1 significantly predicted the composite renal endpoint.
Conclusion: Urine biomarkers of tubular injury effectively identified diabetic patients at elevated risk for CKD progression and death in T2DM patients
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271-81.
Parving HH, Oxenboll B, Svendsen PA, Christiansen JS, Andersen AR. Early detection of patients at risk of developing diabetic nephropathy. A longitudinal study of urinary albumin excretion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1982;100(4):550-5.
Satirapoj B. Tubulointerstitial Biomarkers for Diabetic Nephropathy. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018:2852398.
Perkins BA, Ficociello LH, Silva KH, Finkelstein DM, Warram JH, Krolewski AS. Regression of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(23):2285-93.
Perkins BA, Ficociello LH, Ostrander BE, Silva KH, Weinberg J, Warram JH, et al. Microalbuminuria and the risk for early progressive renal function decline in type 1 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(4):1353-61.
Satirapoj B. Review on pathophysiology and treatment of diabetic kidney disease. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010;93 Suppl 6:S228-41.
Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Brown DM, Mauer SM. An overview of renal pathology in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in relationship to altered glomerular hemodynamics. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992;20(6):549-58.
Satirapoj B, Nast CC, Adler SG. Novel insights into the relationship between glomerular pathology and progressive kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2012;19(2):93-100.
Bohle A, Wehrmann M, Bogenschutz O, Batz C, Muller CA, Muller GA. The pathogenesis of chronic renal failure in diabetic nephropathy. Investigation of 488 cases of diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Pathol Res Pract. 1991;187(2-3):251-9.
Tenstad O, Roald AB, Grubb A, Aukland K. Renal handling of radiolabelled human cystatin C in the rat. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1996;56(5):409-14.
Herget-Rosenthal S, Feldkamp T, Volbracht L, Kribben A. Measurement of urinary cystatin C by particle-enhanced nephelometric immunoassay: precision, interferences, stability and reference range. Ann Clin Biochem. 2004;41(Pt 2):111-8.
Tian S, Kusano E, Ohara T, Tabei K, Itoh Y, Kawai T, et al. Cystatin C measurement and its practical use in patients with various renal diseases. Clin Nephrol. 1997;48(2):104-8.
Graciano ML, Cavaglieri Rde C, Delle H, Dominguez WV, Casarini DE, Malheiros DM, et al. Intrarenal Renin-Angiotensin system is upregulated in experimental model of progressive renal disease induced by chronic inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(7):1805-15.
Ichimura T, Bonventre JV, Bailly V, Wei H, Hession CA, Cate RL, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(7):4135-42.
Grenier FC, Ali S, Syed H, Workman R, Martens F, Liao M, et al. Evaluation of the ARCHITECT urine NGAL assay: assay performance, specimen handling requirements and biological variability. Clin Biochem. 2010;43(6):615-20.
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Yang J, Mitsnefes M, et al. Amelioration of ischemic acute renal injury by neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(12):3073-82.
Satirapoj B, Siritaweesuk N, Supasyndh O. Urinary angiotensinogen as a potential biomarker of diabetic nephropathy. Clin Kidney J. 2014;7(4):354-60.
Satirapoj B, Aramsaowapak K, Tangwonglert T, Supasyndh O. Novel Tubular Biomarkers Predict Renal Progression in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:3102962.
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(9):604-12.
Eddy AA, Neilson EG. Chronic kidney disease progression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(11):2964-6.
Nauta FL, Boertien WE, Bakker SJ, van Goor H, van Oeveren W, de Jong PE, et al. Glomerular and tubular damage markers are elevated in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(4):975-81.
van Timmeren MM, van den Heuvel MC, Bailly V, Bakker SJ, van Goor H, Stegeman CA. Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in human renal disease. J Pathol. 2007;212(2):209-17.
Yang YH, He XJ, Chen SR, Wang L, Li EM, Xu LY. Changes of serum and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in type-2 diabetic patients with nephropathy: one year observational follow-up study. Endocrine. 2009;36(1):45-51.
Kim SS, Song SH, Kim IJ, Yang JY, Lee JG, Kwak IS, et al. Clinical implication of urinary tubular markers in the early stage of nephropathy with type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;97(2):251-7.
Bhavsar NA, Kottgen A, Coresh J, Astor BC. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) as predictors of incident CKD stage 3: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60(2):233-40.
Conti M, Moutereau S, Zater M, Lallali K, Durrbach A, Manivet P, et al. Urinary cystatin C as a specific marker of tubular dysfunction. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2006;44(3):288-91.
Kim SS, Song SH, Kim IJ, Jeon YK, Kim BH, Kwak IS, et al. Urinary cystatin C and tubular proteinuria predict progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(3):656-61.
Viau A, El Karoui K, Laouari D, Burtin M, Nguyen C, Mori K, et al. Lipocalin 2 is essential for chronic kidney disease progression in mice and humans. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(11):4065-76.
Bolignano D, Lacquaniti A, Coppolino G, Donato V, Campo S, Fazio MR, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and progression of chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(2):337-44.
Kaul A, Behera MR, Rai MK, Mishra P, Bhaduaria DS, Yadav S, et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin: As a Predictor of Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Indian J Nephrol. 2018;28(1):53-60.
van Timmeren MM, Bakker SJ, Vaidya VS, Bailly V, Schuurs TA, Damman J, et al. Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 in protein-overload nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;291(2):F456-64.
Panduru NM, Sandholm N, Forsblom C, Saraheimo M, Dahlstrom EH, Thorn LM, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1 and the loss of kidney function in diabetic nephropathy: a likely causal link in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(6):1130-7.
Seibert FS, Sitz M, Passfall J, Haesner M, Laschinski P, Buhl M, et al. Prognostic Value of Urinary Calprotectin, NGAL and KIM-1 in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018;43(4):1255-62.
Hsu CY, Xie D, Waikar SS, Bonventre JV, Zhang X, Sabbisetti V, et al. Urine biomarkers of tubular injury do not improve on the clinical model predicting chronic kidney disease progression. Kidney Int. 2017;91(1):196-203.
Yamamoto T, Nakagawa T, Suzuki H, Ohashi N, Fukasawa H, Fujigaki Y, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a marker of intrarenal angiotensin II activity associated with deterioration of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(5):1558-65.
Juretzko A, Steinbach A, Hannemann A, Endlich K, Endlich N, Friedrich N, et al. Urinary Angiotensinogen and Renin Excretion are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2017;42(1):145-55.
Peralta CA, Katz R, Bonventre JV, Sabbisetti V, Siscovick D, Sarnak M, et al. Associations of urinary levels of kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) and neutrophil gelatinaseassociated lipocalin (NGAL) with kidney function decline in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60(6):904-11.
Kuwabara T, Mori K, Mukoyama M, Kasahara M, Yokoi H, Saito Y, et al. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels reflect damage to glomeruli, proximal tubules, and distal nephrons. Kidney Int. 2009;75(3):285-94.
Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, Thadhani R, Bonventre JV. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. 2002;62(1):237-44.