Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Dry Eye Treatment between Two Severity Assessment Techniques: Measurement of Corneal Epithelial Thickness by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography and Clinical Eye Examination
Main Article Content
Abstract
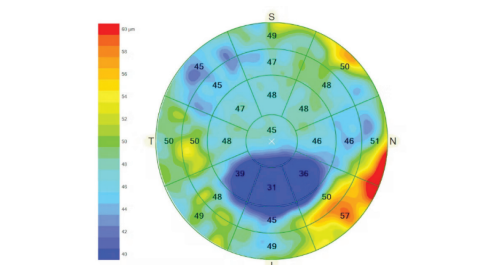
This randomized controlled study was performed to compare the outcome of dry eye treatment between two severity assessment techniques: corneal epithelial thickness (CET) measurement by spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) and clinical eye examination.
The study involved > 18-year-old patients who had been diagnosed with dry eye by the Tear Film & Ocular Surface Society’s Dry Eye Workshop II criteria. Ninety-two patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to the OCT group, in which the severity of dry eye was evaluated with spectral domain OCT,and the control group, in which the severity was evaluated by clinical eye examination. The severityof dry eye was categorized as either mild to moderate or severe. Both groups received 3 months of treatment according to their severity.
The primary outcome was the mean change in the tear breakup time (TBUT) at 1 and 3 monthscompared with baseline. The secondary outcomes were the mean change in the 5-Item Dry Eye Questionnaire (DEQ-5) score and the fluorescein stain grade at 1 and 3 months compared with baseline.
In the OCT group, 28 patients had mild to moderate dry eye and 18 had severe dry eye. In the control group, 31 patients had mild to moderate dry eye and 15 had severe dry eye. Seven patients were lost to follow-up. At 3 months, the mean TBUT was 0.21 seconds higher in the OCT than the control group, but without statistical significance (P = .487). The mean DEQ-5 score was 0.10 points
higher in the OCT than control group, but also without statistical significance (P = .669). The mean fluorescein stain grade was 0.09 points lower in the OCT than the control group, again without statistical significance (P = .245). The agreement between OCT and clinical assessment for diagnosis of severe dry eye was 88.04% (Kappa coefficient, 0.7384), showing good agreement; however, there was no correlation between the TBUT and CET variance at baseline (Pearson’s correlation, 0.0344).
In conclusion, OCT measurement of CET can be used to quantitatively grade the severity of dry eye and has some advantages over clinical eye examination. However, this study showed no superiority of the treatment outcome of dry eye in the OCT group compared with the control group.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Nelson JD, Craig JP, Akpek EK, Azar DT, Belmonte C, Bron AJ, et al. TFOS DEWS II introduction. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):269-75.
Craig JP, Nichols KK, Akpek EK, Caffery B, Dua HS, Joo C-K, et al. TFOS DEWS II definition and classification report. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):276-83.
Willcox MDP, Argüeso P, Georgiev GA, Holopainen JM, Laurie GW, Millar TJ, et al. TFOS DEWS II tear film report. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):366-403.
Sullivan DA, Rocha EM, Aragona P, Clayton JA, Ding J, Golebiowski B, et al. TFOS DEWS II sex, gender, and hormones report. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):284-333.
Stapleton F, Alves M, Bunya VY, Jalbert I, Lekhanont K, Malet F, et al. TFOS DEWS II epidemiology report. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):334-65.
Bron AJ, de Paiva CS, Chauhan SK, Bonini S, Gabison EE, Jain S, et al. TFOS DEWS II pathophysiology report. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):438-510.
Belmonte C, Nichols JJ, Cox SM, Brock JA, Begley CG, Bereiter DA, et al. TFOS DEWS II pain and sensation report. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):404-37.
Chalmers RL, Begley CG, Caffery B. Validation of the 5-Item Dry Eye Questionnaire (DEQ-5): discrimination across self-assessed severity and aqueous tear deficient dry eye diagnoses. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 2010;33(2):55-60.
Walt JG, Rowe MM, Stern KL. Evaluating the functional impact of dry eye: the Ocular Surface Disease Index [abstract]. Drug
Inf J 1997;31:1436.
Gomes JAP, Azar DT, Baudouin C, Efron N, Hirayama M, Horwath-Winter J, et al. TFOS DEWS II iatrogenic report. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):511-38.
Wolffsohn JS, Arita R, Chalmers R, Djalilian A, Dogru M, Dumbleton K, et al. TFOS DEWS II diagnostic methodology report. Ocul Surf 2017;15(3):539-74.
Bron AJ, Evans VE, Smith JA. Grading of corneal and conjunctival staining in the context of other dry eye tests. Cornea
;22(7):640-50.
No author listed. 2007 Report of the Dry Eye Workshop (DEWS). Ocul Surf 2007;5(2):14.
Kansal V, Armstrong JJ, Pintwala R, Hutnik C. Optical coherence tomography for glaucoma diagnosis: an evidence based meta-analysis. PLoS One 2018;13(1):e0190621.
Ruia S, Saxena S, Gemmy Cheung CM, Gilhotra JS, Lai TYY. Spectral domain optical coherence tomography features and
classification systems for diabetic macular edema: a review. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila) 2016;5(5):360-7.
Baghdasaryan E, Tepelus TC, Marion KM, Bagherinia H, Sadda SR, Hsu HY. Evaluation of corneal epithelial thickness imaged by high definition optical coherence tomography in healthy eyes. Cornea 2019;38(1):62-6.
Francoz M, Karamoko I, Baudouin C, Labbé A. Ocular surface epithelial thickness evaluation with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 201125;52(12):9116-23.
Cui X, Hong J, Wang F, Deng SX, Yang Y, Zhu X, et al. Assessment of corneal epithelial thickness in dry eye patients. Optom Vis Sci 2014;91(12):1446-54.
Kanellopoulos AJ, Asimellis G. In vivo 3-dimensional corneal epithelial thickness mapping as an indicator of dry eye: preliminary clinical assessment. Am J Ophthalmol 2014;157(1):63-8.
Liang Q, Liang H, Liu H, Pan Z, Baudouin C, Labbé A. Ocular surface epithelial thickness evaluation in dry eye patients: clinical correlations. J Ophthalmol 2016;2016:1628469.
Wu Y, Wang Y. Detailed distribution of corneal epithelial thickness and correlated characteristics measured with SD-OCT in myopic eyes. J Ophthalmol 2017;2017:1018321.
Çakır B, Dogan E, Çelik E, Babashli T, Uçak T, Alagöz G. Effects of artificial tear treatment on corneal epithelial thickness and corneal topography findings in dry eye patients. J Fr Ophtalmol 2018;41(5):407-11.
Abou Shousha M, Wang J, Kontadakis G, Feuer W, Canto AP, Hoffmann R, et al. Corneal epithelial thickness profile in
dry-eye disease. Eye (Lond) 2020;34(5):915-22.
Baghdasaryan E, Tepelus TC, Marion KM, Bagherinia H, Sadda SR, Hsu HY. Evaluation of corneal epithelial thickness
imaged by high definition optical coherence tomography in healthy eyes. Cornea 2019;38(1):62-6.
Morisky DE, Green LW, Levine DM. Concurrent and predictive validity of a self-reported measure of medication adherence. Med Care 1986;24(1):67-74.
Shimazaki J, Seika D, Saga M, Fukagawa K, Sakata M, Iwasaki M, et al. A prospective, randomized trial of two mucin secretogogues for the treatment of dry eye syndrome in office workers. Sci Rep 2017;7(1):15210.
Pflugfelder SC, Tseng SC, Sanabria O, Kell H, Garcia CG, Felix C, et al. Evaluation of subjective assessments and objective
diagnostic tests for diagnosing tear-film disorders known to cause ocular irritation. Cornea 1998;17:38-56.
Nichols KK, Nichols JJ, Mitchell GL. The lack of association between signs and symptoms in patients with dry eye disease. Cornea 2004;23:762-70.
Wu S, Tao A, Jiang H, Xu Z, Perez V, Wang J. Vertical and horizontal corneal epithelial thickness profile using ultrahigh resolution and long scan depth optical coherence tomography. PLoS ONE 2014;20:e97962.
Ma JX, Wang L, Weikert MP, Montes de Oca I, Koch DD. Evaluation of the repeatability and reproducibility of corneal epithelial thickness mapping for a 9-mm zone using optical coherence tomography. Cornea 2019;38:67-73.
Sella R, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN, Afshari NA. Repeatability and reproducibility of corneal epithelial thickness mapping with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in normal and diseased cornea eyes. Am J Ophthalmol 2019;197:88-97.
Ang BCH, Sng JJ, Wang PXH, Htoon HM, Tong LHT. Sodium hyaluronate in the treatment of dry eye syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2017;7:9013.
Yang Y-J, Lee W-Y, Kim Y, Hong Y. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of hyaluronic acid eye drops for the treatment of dry eye syndrome. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18(5):2383.
Ervin A-M, Law A, Pucker AD. Punctal occlusion for dry eye syndrome: summary of a Cochrane systematic review. Br J Ophthalmol 2019;103(3):301-6.
Lin PY, Cheng CY, Hsu WM, Tsai SY, Lin MW, Liu JH, et al. Association between symptoms and signs of dry eye among an elderly Chinese population in Taiwan: the Shihpai Eye Study. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005;46:1593-8.